clinical exam
Clinical examination
Clinical Exam:
Nose:
External nose: Examine the dorsom for any dorsal hump or dorsal saddling, Ala for any alar flar or alar collapse, Tip for any tip ptosis or tip over or under projection, Columella for any Columellar show or columellar recession. And examine the examine the overall external nose to see if trh nose externally is crooked or straight.
The Vestibule which is the skin lined are of the anterior naris is examined by elevating the tip of th nose by the tip of the left thumb. The vestibule is examined for any furuncle, crusts discharge or debri.
Anterior rhinoscopy is then performed by using the thudicum's killians or pilchards nasal speculum...examine the nasal septum form any deviation, nasal mucosa to see if its pale pink or congested, inferior turbuiinate to see if its normal or hypertrophied and if possible the middle turbinate and middle meatus.
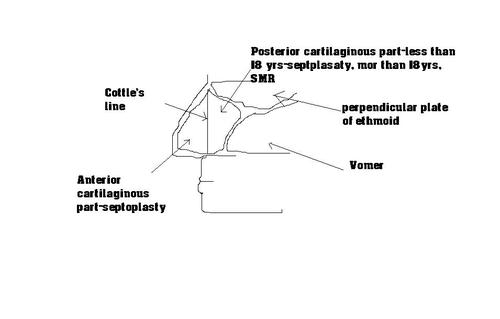
The septum is divided by the cottle's line ;an imaginary vertical line from the nasal spine of frontal to the nasal spine of maxilla into an anterior half and a posterior half. The anterior half is essential to maintain the integrity of the architecture of the external nose and therfore cannot be resected. Deviations in this area are therefore dealt by septoplasty and deviations behind this line can be dealt by submmucosal resection if the patient is above 18 years since the growth has essentially stopped.
The posterior half of the septal cartilage contains a growth center that continues to grow till the age of 18 years...therfore the poserior half should not be resected till that age...if its done, it will lead to developmental hypolasia of the mid third of the face. Hence, posterior septal cartilaginous deviations less than 18 years are to be dealt by septoplasty.
To summarise, anterior septal cartilaginous deviations are dealt by septolasty and posterior deviations are dealt by septoplasty if below 18 years and SMR if above 18years.
After anterior rhinoscopy, posterior rhinoscopy is performed...if found difficult, you may say, posterior rhinospcy was attempted but found difficult because excessive gag reflex.
Then palpation is carried out to find out if the paranasal sinuses are involved. For the frontal sinus palpation is done in the supraorbital area near the medial canthus where the floor of the frontal sinus is , and tenderness is elicited. For the maxillary sinus, the canine fossa is palpated, lateral to the canine eminence and for the ethmoids, the area medial to the medial canthus is palpated. Sphenoid sinus involment is inferred by pain referred to the vertex.
Case Taking:
Long case of ear (Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media)Name: Age and Gender:
Profession:
Address:
- Discharge from ear (Right/left/both): For the last _____ years/months/days
- Difficulty in hearing (Right/left/both ears): For the last _____ years/months/days
- Sensation of imbalance/rotation of self/surroundings: For the last ____ years/months/days
- Pain in the ear/around the ear/headache/neck:
-
-
-
- (Right/left/both): For the last_________ years/months/days
-
-
-
- Perception of sound in the ear in the absence of any external stimulus:
-
- (Right/left/both ears): For the last _____ years/months/days
-
- Facial asymmetry (Right/left/both sides): For the last _____ years/months/days
- Fever: For the last _____ years/months/days
- Which ear? Right/left/both (explain discharge from both ears separately if required)
- Is the discharge more in quantity from one particular ear?
- Since when the ear discharge is occurring (Duration)?
- How did the discharge start (mode of onset)
· Was the onset of discharge preceded by pain
· Or the patient is not aware of how it set in (insidious in onset)
· Any history of trauma to ear (slap injury/blunt trauma/iatrogenic)
- What is the behavior/pattern of ear discharge
· Is it intermittent?
· If intermittent, how does it disappear/reappear? Any relationship with common cold?
· Is it continuous?
- What is the consistency of ear discharge?
· Serous/purulent (Otitis externa)
· Muco-purulent (otitis media)
· Muco-purulent with less mucous content (Attico-antral disease)
- What is the color of discharge?
· Pale white
· Greenish
- What is the amount of muco-purulent discharge?
· Copious (tubo-tympanic)
· Scanty (Attico-antral disease)
- Does the discharge from ear smell foul?
· Yes (Attico-antral disease)/secondary infection with secondary organisms)
· No (Tubo-tympanic disease)
- Is the discharge from ear blood stained?
· Is the blood admixed with discharge/or frank bleeding
· Since how long the discharge has turned blood stained
· Keep in mind:
· Attico-antral pathology
· granulations in middle ear cleft
· change to malignancy
· erosion of a blood vessel
· Is it accompanied by any facial asymmetry
- Patient is suffering from hearing impairment from right/left/both ears?
- If from both ears, which ear has more hearing impairment (usually patient can pinpoint which ear hears well.
- Since how long the hearing impairment is present (duration)?
- How did it start (mode of onset)?
· Sudden (any history of trauma)
· Insidious
- What is the behavior of hearing loss?
· Same as from day one
· Progressive
· Relationship with ear discharge: Improves when ear is filled with muco-purulent discharge and worsens when ear becomes dry
· Episodic
- Can patient listen to conversation carried out in a quiet room?
· Yes (social level of hearing not breached- mild hearing loss)
· No (social level of hearing breached- moderate hearing loss)
- Can patient listen sound of call bell (no-loss around 60 db) and converse on telephone ( no-loss around 70 db)
- Is the patient helped by amplification (ask for behavior changes by patient such as raising the volume of radio/television/does the patient converse softly (as in conductive type of hearing loss) or loud (as in s/n hearing loss)
- Does the patient hear better in noisy surroundings, yes (paracusis willisi) as in conductive type of hearing loss)
- Does the patient have any difficulty in understanding what is being said (speech discrimination)
- Can patient tolerate loud sounds?
Since how long the patient is experiencing imbalance?
How did it set in?
Ask the patient to describe his/her symptoms in own language.
Is it a sensation of spinning/rotation of self or surroundings?
Does the patient tend to fall on one side?
Is this sensation continuous or comes in episodes?
What is the duration of one episode?
Any relationship with neck movements or turning body in the bed?
Is it provoked by exposure to loud noise or pressure changes in the ear?
- Pain in the ear: which side, right/left/both ear
- Since how long the pain is occurring?
- How did it start?
- Any relationship with discharge from the ear?
- Ask the patient to describe the nature of pain: dull, shooting, throbbing
- Ask the patient to grade it on 0-10 Visual analogue scale
- Ask the patient about spread/radiation of pain
- Is it in pre auricular or post auricular area or is it dull headache localized to area around the area?
- Is the patient having headache; generalized or one sided?
- Is it accompanied by neck rigidity?
- Is the pain occurring behind the eye on the corresponding/ ipsilateral side?
- Is the pain extending to upper neck on the corresponding side?
- Is it accompanied by fever with rigor and chills?
- Is it accompanied with any cranial nerve palsy? (Look for it in examination of pt.)
- Since how long the patient is experiencing this symptom?
- How did it set in?
- Ask the patient to describe his/her symptoms in own language.
- Is it dull/ hissing / whistling / throbbing or pulsatile in character?
- Is this sensation continuous or comes in episodes?
- What is the duration of one episode?
- Any relationship with appearance or stoppage of discharge from the ear?
Which side of the face is involved?
When did it set in?
Has there been any improvement since it set in?
When did it start?
Is it accompanied with rigors and chills?
Is it accompanied with headache?
- Previous ear surgery
- Head injury
- Systemic disease (e.g. stroke, multiple sclerosis, cardiovascular disease)
- Ototoxic drugs (antibiotics, diuretics, cytotoxics)
- Exposure to noise at work or recreation (shooting)
- Family history of deafness
- History of atopy and allergy in children
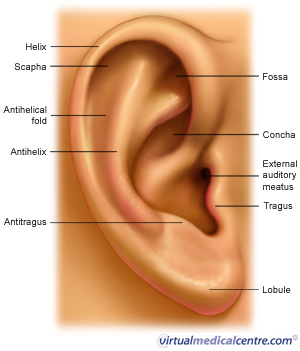
Pinna: Inspect the Pinna for
- Size,
- Shape,
- Overlying skin/skin tags
- Ulcer/inflammation/swelling/scar mark
- Sinus
- Opening of the external auditory canal for size, shape, any narrowing, discharge, any mass (polyp?) presenting at the opening of EAC
Inspect Pre auricular area for any swelling, inflammation, ulceration or scar mark. Pre-auricular sinus
Also inspect the zygomatic area for any swelling, inflammation (Luc’s abscess)
- Any swelling, inflammation, ulceration.
- Post-auricular sulcus for accentuation/obliteration
- Mastoid fistula
- Grissinger’s sign
Pinna:
- Is the local temperature over the pinna raised
- Is its surface smooth
- Are its movements painful
- Is tragal sign positive
- Is the local temperature raised?
- Is there any tenderness present?
- Can you palpate any enlarged pre-auricular lymph nodes?
- Is any pre-auricular sinus present, does any discharge come out of the sinus
- Is it tender
- Is the local temperature over the post-auricular area?
- Is there any tenderness present over the mastoid?
· Look for tenderness at the tip of mastoid.
- Look for tenderness in mastoid emissary vein area
- Is the position of pinna normal?
- What is feel of surface of mastoid: Is it irregular (normal) or is it smooth (ironing out of mastoid surface due to previous mastoiditis resulting in thickening of the periosteum)
- Is the any scar mark seen?
Without speculum: (Pull the pinna upwards, backwards and outwards in any adult and downwards and forwards in an infant)
Comment about:
- Size and shape of EAC. Look for any stenosis or atresia
- Skin of the canal, is it inflamed?
- Any discharge present:
· What is its consistency: serous, muco-purulent, purulent
· Color
· Amount
· Is it foul smelling
· Are any cholesteatoma flakes present
· Is it blood stained
- Clean the discharge, does it refill the canal?
- Is any mass present in the canal? If yes:
· What is it size
· What is its shape
· What is its color
· How is its surface (Smooth/irregular/ulcerated)
· Can the probe be passed around it/ or it is attached one of the walls
· Is it soft/firm or hard
· Is it sensitive to touch
· Is it friable
· Does it bleed on probing
· Does the patient feel any sensation of imbalance when it is manipulated
· Are any facial twitching observed when it is manipulated
- Is any wax or any debris present in the external auditory canal
- Are any granulations present canal and do they bleed on touch?
Comment about skin of deep EAC;
If any discharge/mass present in deep part describe it as above.
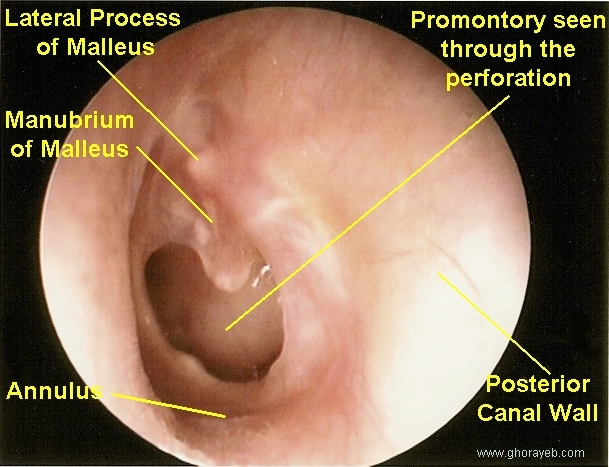
Now look for Tympanic membrane: Comment about:
- Color
- Shape
- Landmarks: Umbo, cone of light, handle of malleus, anterior and posterior malleolar folds, lateral process of malleus
- If the TM is intact
· Is the tympanic thin, atrophied, transparent
· Is it retracted : as a whole or partly (which quadrant)
· What is the degree and scale of retraction or atelectasis
· Do the Seigulisation: is the tympanic membrane normally mobile, retracted in part or whole, is it plastered over the medial wall
· Are any air-bubbles or fluid present behind intact TM
· Any whitish colored mass present behind the intact TN
· Define the position, extent of retraction pockets
· Demonstrate associated bone destruction especially of outer attic wall and postero- superior bony canal
- Is any perforation seen in the TM ; if yes comment about:
· Site (which quadrant or more than one quadrant)
· Size (approximate size in millimeters)
· Shape
· Margins (smooth or irregular)
· Are all the margins around 360 degree seen
· Is the handle of malleus intact or eroded
· Is the tympanic annulus involved
· Is any discharge coming out of perforation
· Is any mass coming out of perforation
· If perforated, differentiate between central and marginal perforation
· If marginal in addition to the characteristics of perforation, demonstrate epithelial ingress into middle ear, if any
· Demonstrate the presence of TM and ME tympanosclerosis
· Assess the status of middle ear mucosa
· Visualise other middle ear structures Ossicles, Eustachian tube, hypotympanic air cells.
Facial nerve examination
ET function tests
Repeat the examination of the second ear
Also examine the nose, throat and neck
Carry out GPE and report before local examination
The patient looks away from the examiner and is asked to repeat a series of numbers or simple words such as ‘cat’ ‘dog’ or house which are whispered into the ear to be tested. Farthest ear distance away from the ear that the words can be just heard is recorded.
The normal ear hears a whisper at five feet (1.5 meter)
The test is carried out in same way, using ordinary speaking voice which a normal ear should hear at thirty feet (9 meters)
Rinne’s Test using TFs of 256, 512, 1024 hertzs
Weber Test 512
A.B.C. 512
Bing’s Test 512
Vestibular function tests:
Spontaneous & induced nystagmus
Ataxia test battery –
- Romberg's
- Tandem Romberg’s
- Unterberger's
- Straight Line Walking
- Tandem Walking
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (Right/left/ both ears)
- Type: Tubotympanic / Attico-Antral (in each ear) with sub-types of each
- With or without deafness (right/left/both ears):
· Type
· Degree (mild, moderate or severe)
- With or without complications
- Otomicroscopy and otoendoscopy
- Ear swab for Gram/Ziel Nielson Staining and culture/ sensitivity
- Patch test
- Pure Tone Audiometry
- Impedance Audiometry
- X'ray both mastoids:
· Law's lateral oblique view
· Schuller's view
· Towne's view
· Per -orbital view
- CT scans/ MRI for evaluating middle ear cleft
Management:
Medical
Surgical
Weber Test
Hearing is tested with a 256-cycles-per-second (cps) or a 512-cps tuning fork. A 128-cps tuning fork measures vibration; it does not test hearing as well. The Weber test places the tuning fork in the center of the forehead and the physician asks the patient where he or she hears it (Fig. 1.1). Is it louder on one side than on the other or is it loudest in the center? With a normal Weber test, the sound is heard loudest in the center or it is heard equally in both ears.

Figure 1.1.
The Weber Test. A 256-cps or 512-cps tuning fork is placed on the forehead and the patient is asked, “Where do you hear that?” Do you hear the noise in the center of your head or is it louder on one side or the other?" The patient may respond, “I hear it right up in front in the center of my forehead.”
With an abnormal Weber test, the sound lateralizes; that is, it is heard louder in one ear. A lateralizing Weber test response is obvious to both patient and physician, but a midline Weber test response can be vague. The patient may not be certain exactly where he or she hears the sound, and it may be necessary to repeat the test several times. A Weber test will lateralize toward an ear with a middle ear conductive hearing loss. To understand this better, place a vibrating tuning fork on your own forehead. Move it to the right and to the left. Note how the sound also moves. Now create a conductive hearing loss by occluding your left external auditory canal with your finger. The sound now lateralizes to your left ear, no matter where on your forehead you place the tuning fork. With a sensorineural hearing loss -- that is, one affecting the cochlea, the acoustic nerve, or, rarely, the brain -- the Weber lateralizes away from the affected ear. If the sensorineural hearing loss is symmetrical, as is found with presbycusis, the hearing loss from aging, the Weber will be midline.
Rinne Test
Sound transmitted through an external ear traverses the middle ear and is perceived by the cochlea (inner ear). Sound can be transmitted directly to the cochlea, skipping the external and middle ear, by placing the vibrating tuning fork on the mastoid bone directly behind the ear. This is the basis for the Rinne hearing test. To perform this test, a 256-cps or 512-cps vibrating tuning fork is placed on the mastoid bone and then moved next to the external ear. The patient indicates at which of the two sites the sound is louder (Fig. 1.2). Normally, air conduction (AC) is greater than bone conduction (BC), a relationship written as Rinne AC > BC.

Figure 1.2.
The Rinne Test. A 256-cps or 512-cps tuning fork is placed first on the mastoid bone (A) and then over the ear canal (B). The patient is asked, “Where is the sound louder: behind your ear or in your ear?” The patient should both hear and feel the vibration in A, and the sound should be louder in B.
If the bone conduction is greater, this implies that there is a conductive hearing deficit; that is, sound is not conducted through the external or the middle ear. Again, you can perform this test on yourself after creating a conductive hearing loss by occluding your left external auditory canal with your finger. Gross hearing can be tested by having the patient listen for the sound of two fingers rubbing together or whispering in the ear or, optimally, by having the patient affirm whether he or she can hear the 256- or 512-cps tuning fork at a very low volume.
Audiometry
An audiogram is the best test for hearing. Air conduction is measured by placing earphones over both ears. Each ear is tested individually to determine its hearing threshold at 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000, 6000, and 8000 cps. Hearing is measured in decibels (dB), which is a logarithmic scale. Thresholds of hearing at 0 to 10 dB represent very good hearing; thresholds at 10 to 30 dB indicate a mild hearing loss; at 30 to 60 dB, there is a moderate hearing loss; at 60 to 90 dB, hearing loss is severe; and when the threshold is greater than 90 dB, the individual is essentially deaf. By convention, air conduction thresholds for the right ear are indicated on the audiogram by the symbol "O" and for the left ear by an "X." Sensorineural hearing measures cochlear, eighth cranial nerve, brain stem, and cerebral auditory function. Sensorineural hearing is measured by placing a bone-conducting vibrator on the mastoid bone behind the ear. The same sound frequencies (250-8000 cps) are measured. Bone conduction on the right is indicated by the symbol "[" and on the left by the symbol "]." If air and bone conduction coincide, the air conduction is also a measure of sensorineural hearing and the bone conduction results are not recorded. Air conduction can never be better than bone conduction (sensorineural hearing). If air conduction is normal, it is not necessary to test bone conduction; only the air-conduction results are recorded.
Some patients have no trouble hearing pure tones, but still have difficulty hearing others talk. This is measured on the audiogram as speech reception threshold (SRT) and is recorded as a single number in decibels. The patient's ability to discriminate different words is also measured as discrimination ability and is recorded as a percentage. Discrimination percentages from 80% to 100% are considered good, 60% to 80% are acceptable, and less than 60% is poor. Figure 1.3 shows a normal audiogram.
Several variations and combinations of tuning fork and audiogram results can be found. Table 1.1 summarizes the Weber and the Rinne tuning fork tests found in clinical medicine. Tuning fork tests are not 100% reliable, but are a useful screening examination. They should correlate with the audiogram; if they do not, the tuning fork tests or the audiogram, or both, should be repeated until the results all appear consistent. The following five cases illustrate some potential tuning fork and audiogram results.

Figure 1.3.
A standard audiogram report from a patient with normal hearing, good speech reception thresholds (SRT), and good word discrimination (Discrim). The sound levels are measured in decibels and recorded vertically. The different frequency sounds are recorded horizontally and measured in cycles per second (cps). The lower limits of normal hearing are indicated by the dashed line at about 25 dB.

A patient complains of decreased hearing in the left ear. The Weber test lateralizes to the left. Rinne test, BC > AC AS and AC > BC AD. (AS means auris sinister [left ear], AD means auris dexter [right ear], and AU means auris unitas [both ears]). The results suggest that the patient has a conductive hearing loss in the left ear (Fig. 1.4). The tuning fork tests and the audiogram demonstrate that this patient has a left ear conductive hearing loss. The SRT on the right is 5 dB, which is normal. On the left side the SRT is decreased to 20 dB, which is expected because of the left ear hearing loss. Discrimination in both ears, measured at 15 dB above the respective SRTs, is 96%, an excellent result. |
Another patient complains of decreased hearing. Both ears seem equally involved. The Weber test is midline and bone conduction is greater than air conduction in both ears, suggesting a bilateral conductive hearing loss. The audiogram for this patient is shown in Figure 1.5. |
A third patient complains of decreased hearing in the left ear. The Weber test lateralizes to the right ear. The Rinne test shows AC > BC AU. This suggests a left sensorineural hearing loss. The audiogram for this patient is shown in Figure 1.6. The tuning fork tests and the audiogram demonstrate that this patient has a left inner ear hearing loss (sensorineural hearing loss). The SRT in the right ear is 5 dB. The SRT in the left ear is decreased to 30 dB. Discrimination in the right ear is 96% when measured at 15 dB louder than the SRT. Discrimination in the left ear is decreased; it is 50% when measured at 15 dB louder than the SRT and 65% when measured at 40 dB louder than the SRT. |

Figure 1.4.
Audiogram of person with conductive hearing loss in the left ear. SRT = speech reception threshold; Discrim. = word discrimination.

Figure 1.5.
Audiogram of patient complaining of decreased hearing. SRT = speech reception threshold; Discrim. = word discrimination.

Figure 1.6.
Audiogram of patient complaining of decreased hearing in left ear. SRT = speech reception threshold; Discrim. = word discrimination.
A fourth patient complains of decreased hearing in both ears. The Weber test is midline, and the Rinne test shows AC > BC AU. This suggests a bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. The audiogram for this patient is shown in Figure 1.7. The audiogram confirms the tuning fork tests. The SRTs are elevated in both ears, which is to be expected with this hearing loss. The discrimination is normal. |
The last patient complains of decreased hearing in both ears. The Weber test is midline, and the Rinne test shows AC > BC AU. The audiogram reproduced in Figure 1.8 shows a moderate sensorineural hearing loss. Poor discrimination is noted. The patient hears pure tones satisfactorily, but cannot discriminate words. The ultimate effect is that the individual does not perceive language. |

Figure 1.7.
Audiogram of a patient with decreased hearing in both ears. SRT = speech reception threshold; Discrim. = word discrimination.

Figure 1.8.
Audiogram of a patient with decreased hearing in both ears. SRT = speech reception threshold; Discrim. = word discrimination.
Other Tests of Hearing
When patients have mixed hearing losses -- that is, conductive and sensorineural -- tuning fork test results can be confusing. An audiogram will be necessary to determine the nature of these hearing losses. Additional tests are available and compliment the audiogram.
Tympanometry measures the sound transmitted by the tympanic membrane at different middle ear pressures. It is useful for distinguishing different causes of conductive hearing losses and for measuring middle ear pressures. It also identifies the presence or absence of the stapedial reflex, which is a seventh cranial nerve function.
Brain stem-evoked-response audiometry (BERA) measures nerve potentials from the eighth cranial nerve and from the brain stem. It is useful for testing hearing in infants and for detecting cerebellopontine angle tumors. Brain stem-evoked-response audiometry is an important addition to the neurotologic evaluation. This method does not require subjective patient responses, as does standard pure tone audiometry. It is useful in localizing retrocochlear causes of sensorineural hearing loss. Figure 1.9 shows a normal tracing and correlates the different waves with their presumed respective anatomic origins. Both the waveforms and their respective latencies are important.
The electronystagmogram is useful in measuring vestibular function.
Anatomy of the Ear and Mechanism of Hearing
The anatomy of the ear should be known to all who deal with hearing disorders, but basic structures are reviewed here so that all will use the same terminology (see Fig. 1.10). The external ear canal is supported by cartilage laterally and by bone medially. Hairs and cerumen glands are present in the lateral third of the ear canal. The tympanic membrane, which lies at the medial end of this "sound tunnel," is very thin and supported about its circumference by a bony annulus. In this center, the tympanic membrane is attached firmly to the malleus. The middle ear is a small cavity connected with the nasopharynx through the Eustachian tube. It is continuous with the mastoid air cells behind the ear. The middle ear contains three small ear bones: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. Sound transmitted through the external auditory canal causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate. This vibration is transmitted through and amplified 20 times by the middle ear (tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, and stapes). Sound enters the inner ear through the oval window. The sound is then perceived by the hair cells in the inner ear (cochlea) and is transmitted to the brain by the eighth cranial nerve. The round window is connected to the cochlea and is responsible for equalizing inner ear pressure. The vestibular system, containing the semicircular canals, is responsible for balance. It is intimately connected to the cochlea. The signals of the vestibular system to the brain are also carried by the eighth cranial nerve. The facial nerve runs through the inner ear, middle ear, and mastoid. The carotid artery, sigmoid sinus, and jugular bulb also course through the temporal bone.

Figure 1.9.
Anatomic correlation of audiometric brainstem-evoked-response potentials. (Used with permission of Dr. Jeffrey P. Harris.)
Physical Examination of the Ear
Physical examination of the ear is difficult. While the auricle and the lateral external ear canal are easily seen, visualization of the medial external ear canal and tympanic membrane requires an otoscope. The normal tympanic membrane is translucent and gray in color, and may have vascular streaks along the malleus.

Figure 1.10.
Anatomy of the Ear
If the tympanic membrane is inflamed, as in otitis media, it thickens and loses its transparency. As it becomes increasingly inflamed, it becomes erythematous. The normal tympanic membrane lies in a neutral position. In otitis media, the middle ear contains a purulent exudate under pressure which bulges the drum laterally. In serous otitis media, conversely, the middle ear has a decreased pressure and the drum is retracted medially. Drum position is difficult to determine with monocular vision. Incidentally, the presence of a light reflex has no meaning except to let you know you remembered to turn on the light on your otoscope.
Pneumomassage will help in evaluation of middle ear pressure. The otoscope speculum is placed so it gently seals the external ear canal. When the bulb on the otoscope is gently squeezed, the drum should visibly move away (medially) and then back (laterally). This is called normal movement to pneumomassage. If the drum is already retracted medially, it will not move when the bulb is squeezed. When the bulb is released, a negative pressure is created, and the drum moves laterally for an instant and then quickly back to its retracted position. This is called reverse movement to pneumomassage and is diagnostic of negative middle ear pressure. If the drum is under pressure and bulging laterally, it will not move at all to pneumomassage. Figure 1.11 illustrates these situations.

Figure 1.11.
Pneumomassage. A great deal can be learned about the middle ear by applying pressure to the tympanic membrane, a procedure called pneumomassage. If it is done correctly, three different responses can be seen as depicted here. A severe negative pressure can pull the eardrum medially, and it too may exhibit no movement on pneumomassage.
If a perforation is seen, its position and size should be noted. It is best to draw a picture of the drum and the perforation. It should be noted if the perforation extends to the margin or annulus of the drum (marginal perforation). Perforation that does not extend to the margin is called a central perforation. Figure 1.12 illustrates the most common perforations.

Figure 1.12.
Tympanic membrane perforations. If a tympanic membrane perforation is seen, you should draw a simple picture, estimate its size (in percentage), and indicate whether it is marginal or central.
Examination of the Nose
If the external nose is deformed, it should be indicated; if not, it need not be mentioned. The interior of the nose should be examined either with a nasal speculum or otoscope speculum. If a speculum is used for the nose, it should be disposable or carefully washed with soap and water, alcohol, or other disinfectant between patients.
The septum and the middle and inferior turbinates should be visible. The mucosal color must be examined; infection or irritation turns the mucosa red (erythema). Allergy swells the mucosa and it appears pale or bluish in color. Polyps or tumors must be looked for deep in the nose. Today, the nasal cavity is best examined with a flexible or rigid endoscope. The flexible scopes are easier to use and provide a view of the larynx, as well.
Examination of the Throat (Oral Cavity, Oropharynx, Larynx, and Neck)
The nasopharynx can only be examined with special endoscopic instruments or a headlight and a mirror. This normally is not part of a routine physical examination except when performed by a head and neck surgeon.
The oral cavity is examined by inspection and palpation. The mucosal surfaces and the patient's teeth are examined. The tonsils, the palate, and the pharynx must be visually examined. Palpate the palate, the cheeks, the tongue, the floor of the mouth, and the lips. If a pathologic condition exists in the posterior pharynx or nasopharynx, it should also be palpated. Check the uvula. An edematous uvula means the patient snores and may have sleep apnea.
The larynx is examined with endoscopic instruments or with a mirror and headlight. Most physicians do not routinely examine the larynx, but the techniques can be learned from any head and neck surgeon.
The neck is examined by palpating the pertinent structures in a routine systematic fashion. The posterior triangles are palpated while standing in front of the patient. The anterior triangles are palpated while standing behind the patient, beginning with the submental area. The submandibular gland can be located high under the mandible or can be ptotic, that is, hanging down lower in the neck. The hyoid, thyroid, and cricoid cartilages are palpated, followed by the internal jugular lymph node chain and finally the thyroid gland. The posterior cervical triangle is palpated, feeling for lymph nodes and abnormal masses. The area over the carotids is auscultated for bruits.
As stated at the start of this chapter, the examination is complex. Guidance and practice are needed to achieve competence.